What is Radiation Dermatitis?
Posted by Amanda Barrell and Reviewed by Cynthia Cobb, APRN on Oct 3rd 2018
Radiation dermatitis is one of the side effects of cancer treatment radiotherapy that people experience most often.
Also known as radiodermatitis, it happens when radiation therapy damages the outer layers of a person's skin.
An estimated 95 percent of people who receive radiation therapy will have some form of radiation dermatitis, including redness, skin dryness, or skin peeling.
This article explores radiation dermatitis, including what causes it, and how people can ease the symptoms at home.
What is radiation dermatitis?

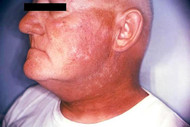
Radiotherapy may cause radiation dermatitis.
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967
Radiation dermatitis is a common side effect of radiotherapy, which is one of the most frequently used treatments for cancer.
Radiation dermatitis can vary in severity. Some people will experience mild redness and itchiness, while others may suffer painful, broken skin that is prone to infection.
The effects of radiation dermatitis typically arise within a few days or weeks of starting radiotherapy, depending on the dose of radiation, and a person's skin sensitivity.
The symptoms only appear on the areas of skin that doctors had to expose to the radiation.
Symptoms of radiation dermatitis
Symptoms of radiation dermatitis include:
- skin redness or pinkness, known as erythema
- skin swelling, or edema
- dry, peeling skin, called dry desquamation
- skin that thins and weakens called moist desquamation
- blisters or skin ulcers
The severity of radiation dermatitis varies between people and radiation doses in the following grades:
- Grade 1, faint redness and skin peeling
- Grade 2, moderate redness and swelling, skin thinning in the skin folds
- Grade 3, skin thinning more than 1.5 centimeters across, not just on the skin folds, plus severe swelling
- Grade 4, death of skin cells and deep skin ulcers
Sometimes, these effects can also develop weeks or years after radiotherapy has finished. This is called radiation recall.
In severe cases, the symptoms can restrict movement in the affected limb, which can interfere with day-to-day activities. People may find it difficult to wear clothes on the sensitized areas.
Causes

Radiation therapy can destroy cancer cells.
Radiation therapy is when doctors use high-energy waves, such as X-rays, or gamma rays, to destroy or damage the cancer cells. These rays make tiny breaks in the DNA inside the cells, stopping it from growing and dividing.
During the treatment, doctors also unavoidably expose normal cells that are near the cancer cells to the radiation. This includes skin cells, and the damage causes radiation dermatitis.
In most cases, the cells will recover and return to normal after the course of radiotherapy has finished.
Risk factors
The likelihood of developing radiation dermatitis during radiotherapy depends on several things. These are called risk factors. People have a higher chance of skin problems if they are:
- older
- malnourished
- a smoker
- have overlapping skinfolds
- have poor skin strength before radiation therapy
- obese
- undergoing chemotherapy also
- have another health condition, such as diabetes or kidney failure
Genetics also play a role, meaning some people are more susceptible to radiation dermatitis than others.
The type of radiotherapy someone has, as well as how and to which part of the body doctors deliver it, can also make a difference. People are more likely to get radiation dermatitis if their treatment involves the following:
- high doses of radiotherapy
- radiotherapy on a large area of the body
- radiotherapy over a long period of time
Radiation to the head, neck, breast, chest wall, the vulva or near the anus is more likely to cause radiation dermatitis.
Skincare
Radiation dermatitis is a common side effect of radiotherapy, which can damage skin cells as it fights cancer cells. Symptoms include redness, skin peeling, and ulceration. It usually begins to resolve after treatment ends. In some cases, it can appear years after radiotherapy has finished.
People can treat the symptoms of radiation dermatitis at home using soothing skincare routines. Healthcare teams may also provide creams and other treatments. Learn more here @ Medical News Today